What is Compositing?
VFX Compositing is the art of combining multiple visual elements from different sources into a single image, creating a seamless, cohesive final product. This technique has been a cornerstone of visual storytelling for decades, enabling filmmakers, advertisers, and photographers to bring their creative visions to life. From the earliest days of cinema to today’s high-tech digital landscapes, compositing has played a crucial role in the visual arts.
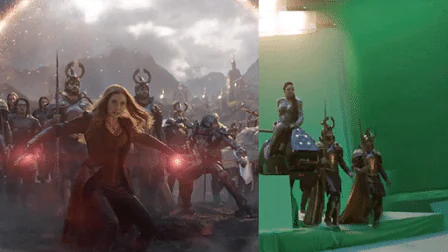
Importance in Visual Arts and Media
Nowaday’s in digital age, the importance of compositing cannot be overstated. It is an essential skill for anyone involved in visual media, from blockbuster movies and television shows to advertisements and digital marketing campaigns. The ability to blend different elements seamlessly can turn an ordinary scene into something extraordinary.
Understanding the Basics
Key Concepts in Compositing
Layers and Masks
Layers are the building blocks of any composite image. Each layer represents a different element of the final image, and masks are used to control which parts of a layer are visible or hidden. This allows for precise control over the composition and blending of elements.
Blending Modes
Blending modes determine how layers interact with each other. By changing the blending mode, you can create different visual effects and seamlessly integrate multiple elements into a single image.
Matte Extraction
Matte extraction is a technique used to isolate specific parts of an image, such as a person or object, from its background. This is often used in green screen and chroma keying processes.
Tools and Software
Popular Compositing Software
Adobe After Effects
Adobe After Effects is a powerful tool for creating stunning visual effects and motion graphics. Its user-friendly interface and extensive features make it a favorite among professionals and amateurs alike.
Nuke by Foundry
Nuke is a node-based compositing software widely used in the film and television industry. It offers advanced features and flexibility, making it ideal for complex compositing tasks.
Blackmagic Fusion
Blackmagic Fusion is another node-based compositing software known for its robust features and integration with other Blackmagic Design products. It is widely used in post-production for film, television, and commercials.
Comparison of Features
User Interface
- Adobe After Effects: Intuitive and user-friendly
- Nuke: Advanced, node-based interface
- Blackmagic Fusion: Versatile and integrated with other Blackmagic products
Functionality
- Adobe After Effects: Excellent for motion graphics and basic compositing
- Nuke: Best for complex, high-end compositing
- Blackmagic Fusion: Comprehensive toolset for VFX and compositing
Pricing and Accessibility
- Adobe After Effects: Subscription-based, accessible for individuals and small studios
- Nuke: Higher cost, aimed at professional studios
- Blackmagic Fusion: Competitive pricing, suitable for various budgets
Techniques in Compositing
Layer-based Compositing
Layer-based compositing involves stacking multiple layers on top of each other, with each layer representing a different element of the final image. This method is intuitive and widely used in applications like Adobe After Effects.
Practical Examples and Applications
- Combining live-action footage with CGI
- Adding text and graphics to videos
- Creating complex visual effects by layering multiple elements
Node-based Compositing
Node-based compositing uses a network of nodes to represent different elements and operations. This method offers greater flexibility and control, making it ideal for complex compositing tasks.
Pros and Cons Compared to Layer-based Compositing
- Pros: Greater control and flexibility, ideal for complex projects
- Cons: Steeper learning curve, more complex interface
Green Screen and Chroma Keying
Green screen and chroma keying techniques are used to remove backgrounds from footage, allowing you to replace them with different images or video. This is a fundamental skill in compositing, used extensively in film and television production.
Techniques for Removing Backgrounds
- Lighting the green screen evenly
- Using keying software to isolate the subject
- Refining the matte to ensure clean edges
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Spill: Adjusting key settings to reduce green edges around the subject
- Shadows: Ensuring even lighting to avoid shadows on the green screen
- Edge Detail: Using matte refinement tools to achieve clean, sharp edges
Applications of Compositing
Film and Television
Compositing is a vital tool in film and television production, used to create stunning visual effects and integrate CGI with live-action footage.
Special Effects and CGI Integration
- Creating realistic explosions and other effects
- Integrating CGI characters into live-action scenes
- Enhancing environments with digital set extensions
Case Studies of Famous Movies and TV Shows
- “Avatar”: Extensive use of compositing to blend live-action and CGI elements
- “The Mandalorian”: Innovative use of virtual sets and real-time compositing
Advertising and Marketing
In advertising and marketing, compositing is used to create compelling visual content that captures the audience’s attention.
Creating Compelling Visual Content
- Combining product shots with dynamic backgrounds
- Adding motion graphics and text to enhance messages
- Using visual effects to create memorable ads
Examples from Successful Ad Campaigns
- Apple’s “Shot on iPhone” campaign: Seamless integration of footage and graphics
- Coca-Cola’s holiday ads: Combining live-action and CGI elements to create magical scenes
Photography
Compositing techniques are also used in photography to enhance images and create unique visual effects.
Enhancing Images with Compositing
- Combining multiple exposures for HDR images
- Adding elements to photos to create surreal scenes
- Removing unwanted objects from images
Techniques for Seamless Integration
- Matching lighting and color
- Using masks and blending modes to merge elements smoothly
- Refining edges and details to ensure a natural look
Advanced Compositing Techniques
3D Compositing
3D compositing involves integrating 3D elements with 2D footage, creating a more immersive and realistic final image.
Integrating 3D Elements with 2D Footage
- Importing 3D models into compositing software
- Matching camera angles and lighting
- Using depth maps to blend 3D elements with 2D footage
Software and Tools for 3D Compositing
- Adobe After Effects with Element 3D plugin
- Nuke with 3D compositing features
- Blackmagic Fusion’s 3D workspace
Motion Tracking and Match Moving
Motion tracking and match moving techniques are used to track the movement of objects in footage, allowing you to add digital elements that move in sync with the live-action.
Techniques for Tracking Movement
- Using point tracking to follow specific points in the footage
- Applying tracking data to digital elements
- Refining tracks to ensure accuracy
Applications in VFX
- Adding digital elements to moving shots
- Stabilizing shaky footage
- Creating complex camera moves in post-production
Color Grading and Correction
Color grading and correction are essential steps in the compositing process, ensuring that all elements of the final image have a consistent look and feel.
Importance of Color in Compositing
- Enhancing the mood and atmosphere of the scene
- Ensuring visual continuity between different elements
- Correcting color imbalances and matching tones
Tools and Techniques for Color Grading
- Using color correction tools in compositing software
- Applying color grading presets and LUTs
- Adjusting contrast, saturation, and hue to achieve the desired look
Tips and Best Practices
Planning Your Composite
Proper planning is crucial for a successful composite. This involves storyboarding, pre-visualization, and gathering all necessary resources and assets before starting the compositing process.
Storyboarding and Pre-visualization
- Sketching out the final image
- Identifying key elements and their positions
- Planning the sequence of compositing steps
Gathering Resources and Assets
- Collecting high-quality images, footage, and 3D models
- Organizing assets for easy access
- Ensuring all elements are properly lit and shot
Attention to Detail
Paying attention to detail is essential for creating seamless composites. This involves careful masking, precise blending, and refining edges to ensure all elements integrate smoothly.
Ensuring Seamless Integration
- Matching lighting and shadows
- Using edge refinement tools to create clean transitions
- Adjusting colors and tones to ensure consistency
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Overlooking small details that break the illusion
- Using low-quality assets that stand out
- Failing to match lighting and perspective
Continuous Learning
Compositing is a constantly evolving field, with new tools and techniques emerging regularly. Staying updated with industry trends and continuously learning is key to maintaining and improving your compositing skills.
Staying Updated with Industry Trends
- Following industry blogs and forums
- Attending workshops and conferences
- Participating in online communities
Resources for Further Learning
- Online tutorials and courses
- Books and eBooks on compositing techniques
- Websites and blogs dedicated to visual effects and compositing
Conclusion
The Future of Compositing
The future of compositing is bright, with emerging technologies and trends promising to push the boundaries of what is possible. From real-time compositing in virtual production to advancements in AI-driven visual effects, the field is constantly evolving.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
- Real-time compositing in virtual production
- AI-driven visual effects and automation
- Improved tools for 3D compositing and motion tracking
The Evolving Role of Compositing in Digital Media
As digital media continues to grow, the role of compositing becomes increasingly important. Whether it’s creating stunning visual effects for films or enhancing images for advertising, compositing is a vital skill in the digital age.
Final Thoughts
Encouraging experimentation and creativity is crucial for anyone interested in compositing. The possibilities are endless. If you are looking for Compositing Service you can contact us.

